Proximate and Organoleptic Levels of Tempeh Made from Cowpeas from Southwest Maluku and Its Integration in Community Learning
Abstract
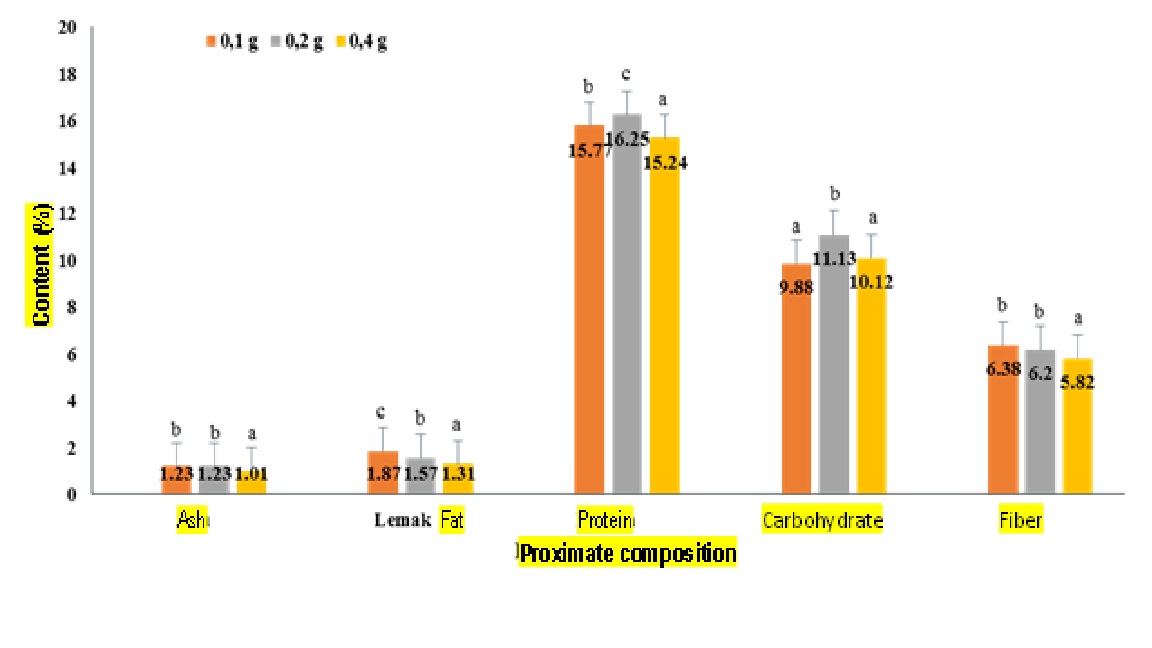
Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) is a type of bean that is well known and developed in Indonesia. One area in Indonesia that has the potential for these nuts is Southwest Maluku. Utilization in local communities is still limited. Therefore, the development of food products such as tempeh is considered. In making tempeh, the dosage of yeast determines the success of fermentation. To be suitable for consumption, nutritional and organoleptic composition testing is required. Thus, this research aims to analyze the proximate and organileptic levels of tempeh made from cowpeas from Southwest Maluku. The study used a Completely Randomized Design treatment with a yeast dose of 0.1 g; 0.2g; 0.4 g repeated 3 times. The data obtained were analyzed using the Anova test (one way) and continued with the DMRT test on SPSS software version 26.0. The research results showed that yeast dosage had a significant effect on ash, fat and fiber content and had high organoleptic value. Treatment two (P2) has a high nutritional composition and the best organoleptic value compared to other treatments. Thus, tempeh made from cowpeas from Southwest Maluku with a yeast dose of 0.2 g can be recommended for development as a food product for the people of Southwest Maluku.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2024 wa ode karmila

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with BIOEDUPAT: Pattimura Journal of Biology and Learning agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.








 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a 