Radioisotope 32P for Keloid Therapy: A Review
Abstract
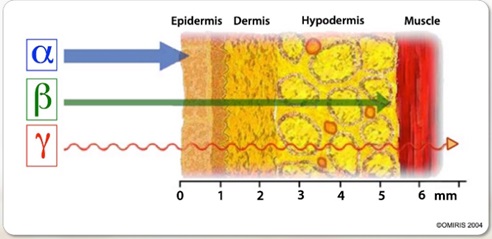
Keloids are skin disorders resulting from an abnormal wound healing response, often leading to excessive scar tissue growth. Keloids can be itchy, painful, and aesthetically disturbing. Keloid therapy varies, but until now, there is no standard method that is effective due to different patient responses. Racial, environmental, and genetic variables influence keloids. Various therapeutic techniques, such as surgery, cryotherapy, corticosteroid injections, laser light, and radiotherapy, have been used to treat keloids, but each has advantages and disadvantages. However, these treatments have limitations, such as high recurrence rates and patient discomfort. The application of radioisotope therapy, specifically using 32P, has emerged as a promising alternative. Radioisotope 32P emits β-particles, effectively inhibiting keloid cell growth by causing DNA damage and reducing collagen production. Studies show that 32P therapy significantly reduces keloid size and recurrence rates while causing minimal patient discomfort. Although there are potential risks, such as damage to surrounding healthy tissue, 32P therapy provides a practical and non-invasive option for keloid management. However, more research is required to fully understand this method’s effectiveness, safety, and long-term impact on keloid therapy, optimize treatment protocols, and minimize side effects.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2024 Wira Y Rahman, Budiawan Budiawan, Heny Suseno

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Copyright on any article is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal, the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





_copy1.png)










