Iron Doped Calcium Manganese Oxide Cathode Materials for Aqueous Zinc Secondary Batteries
Abstract
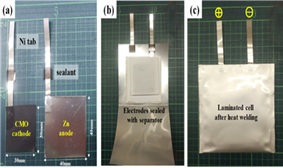
In recent years, zinc secondary batteries, which utilize a water-based electrolyte and offer high safety, have attracted attention as post-lithium-ion batteries. Zn has a high specific capacity (820 mAh/g) and a redox potential of -0.76 V (versus the standard hydrogen electrode) as a cathode. Furthermore, combining it with new cathode materials could significantly enhance performance. In particular, layered compounds containing manganese are inexpensive, widely used in industry, and considered promising candidates. This study synthesized calcium manganese oxide with a layered structure and investigated its potential as a cathode material for zinc secondary batteries. It is already known that Ca₂Mn₃O₈ has a layered structure and can be synthesized with a Mn/Ca atomic ratio ranging from 1.5 to 2.5. This research examined the effect of adding Fe and Al to this calcium manganese oxide on battery performance. When Fe was added, the battery capacity increased by 20%, reaching 177 mAh/g compared to the sample without Fe. This increase is believed to result from an increased interlayer distance, promoting the incorporation of structural water and enhancing ion conversion reactions during charge and discharge. However, adding Al was found to have no beneficial effect on battery performance.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2025 Gota Asano, Yoshiyuki Kojima

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Copyright on any article is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal, the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





_copy1.png)










