Investigation of Pharmacokinetics, Molecular Docking, and Dynamics of Xanthomicrol-Derived Compounds Against Various Mutated Proteins in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
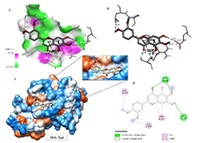
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of global mortality, primarily due to drug resistance and the adverse effects of conventional therapies. Therefore, the discovery of novel compounds that are both effective and safe is crucial for the development of alternative treatments. This study employed a computational approach to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Xanthomicrol-derived compounds targeting mutated proteins commonly associated with lung cancer. Four derivatives (u1a, u2a, u3a, and u4a) were assessed using pharmacokinetic (ADMET) predictions, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations against ten mutated lung cancer-related proteins (1nq1, 1x2j, 4b3z, 4j97, 5l2q, 6pwa, 6usx, 7pgk, 7pgl, and 7r7k). ADMET predictions revealed that all compounds had good gastrointestinal absorption, did not cross the blood–brain barrier, and exhibited favourable safety profiles. Among them, compound u3a showed the highest binding affinity toward seven mutated proteins, with docking scores ranging from -5.9 to -9.4 kcal/mol. Molecular dynamics simulations further supported the stability of u3a protein interactions, indicated by low RMSF values and an optimal radius of gyration. These results suggest that u3a is a promising candidate for targeted lung cancer therapy and warrants further experimental validation.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Akbar S Kurniawan, Muhamad Jalil Baari, Laili Cahyani Sabila, Rana Triana Amin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Copyright on any article is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal, the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





_copy1.png)










