Physicochemical Characterization and Recyclability of CaO/SiO₂ Catalysts Derived from Eggshell and Rice Husk for Biodiesel Application
Abstract
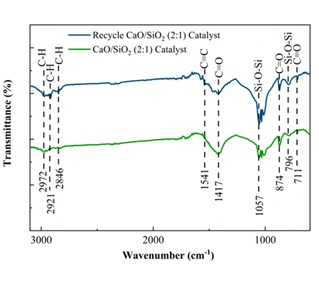
This study aims to evaluate the physicochemical characteristics and reusability of CaO/SiO₂ heterogeneous catalysts synthesized from eggshell and rice husk waste for biodiesel production. The catalyst, prepared with a 2:1 CaO to SiO₂ ratio, was applied in three transesterification cycles using waste cooking oil. Between cycles, the used catalyst was washed with n-hexane and dried at 80 °C for 12 hours. Catalyst characterization was performed using SEM-EDX, FTIR, and N2 adsorption-desorption analysis. The biodiesel yield decreased from 65 ± 4.95% (first cycle) to 54 ± 1.41% and 46 ± 2.12% in subsequent cycles, indicating reduced catalytic activity. SEM-EDX revealed particle agglomeration, calcium content declined (from 24.78% to 19.22%), and increased silicon exposure (from 4.66% to 21.86%). FTIR analysis detected organic residue accumulation, while N2 adsorption-desorption results showed a decrease in surface area (20.79 to 11.67 m²/g) and pore volume (0.03 to 0.02 cc/g), with increased pore size. The biodiesel showed a density of 1112–1119 ± 1.41 kg/m³ and a kinematic viscosity of 2.03–2.07 cSt, indicating it still requires purification to meet SNI 7182:2015 standards. These findings highlight the catalyst's promising initial performance and underscore the need for regeneration strategies to maintain catalytic efficiency over multiple uses.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2025 Eti Ayu Nurhana, Meka Saima Perdani, Hilman Imadul Umam, Amalia Dian Fadilla, Christin Octaviani Sitanggang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Copyright on any article is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal, the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





_copy1.png)










