Characterization and Identification Compounds of Liquid Smoke from Used Tire Waste Pyrolysis
Abstract
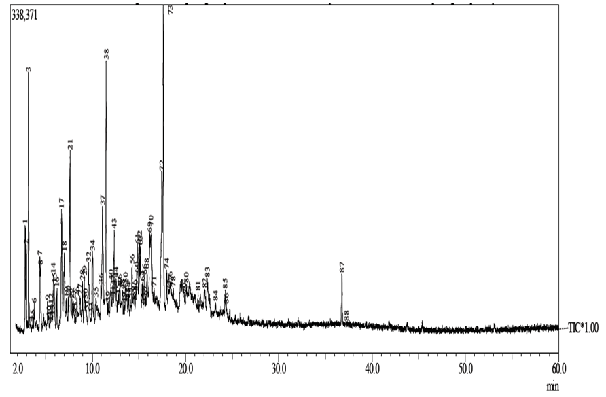
Research on compounds from liquid smoke resulting from the pyrolysis of used tire waste has been conducted. The results of tire pyrolysis produce liquid hydrocarbons and charcoal which can be utilized and developed into more useful materials or finished goods. This study aims to identify the compound components of liquid smoke resulting from the pyrolysis of used tire waste. The research begins with manufacturing a pyrolysis tool based on the principle of dry distillation. The pyrolysis process is carried out by heating at high temperatures. Liquid smoke analysis was carried out using GC-MS. In contrast, the components of the compound were identified and characterized by comparing the mass spectrum data obtained with the mass spectrum data in the GC-MS library. The results showed that the pyrolysis of 6 kg of used tires produced 1500 mL of liquid smoke. Analysis of liquid smoke by GC-MS produced 88 chromatogram peaks, with the most dominant peak height at peaks 3, 17, 37, 38, 72, and 73. The most dominant compound component identified by MS spectrum analysis is 2-propanone (peak 3), 4-methyl-2-pentanone (peak 17), ethyl-benzene (peak 37), 1,2-dimethyl-benzene (peak 38), 1-methyl-4-(1-methyl ethyl)-benzene (peak 72) and limonene (peak 73).
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2023 Johny Zeth Lombok, I Dewa Ketut Anom

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Copyright on any article is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal, the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





_copy1.png)










