Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity of Honey Derived from Bone, South Sulawesi, Indonesia
Abstract
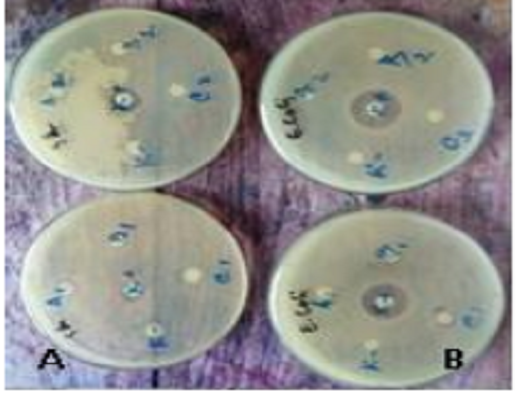
Honey is a sweet substance produced by honey bees from the nectar of flowers or other parts of plants. Honey obtained from Bone, in South Sulawesi, has been extracted and tested for antibacterial activity and toxicity. Honey was macerated with methanol to obtain a crude extract. Methanol crude extract was then partitioned successively with n-hexane and ethyl acetate to obtain ethyl acetate and methanol fraction. Antibacterial activity test was performed by agar diffusion method against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Methanol extract, ethyl acetate fraction, and methanol fraction showed an inhibition zone against E. coli at 10.10, 10.05, and 8.40 mm, respectively with amoxicillin as a positive control (20.05 mm). Also against S. aureus, inhibition zone was obtained at 11.90, 9.30, 8.60, and 13.70 mm for methanol extract, ethyl acetate fraction, methanol fraction, and amoxicillin, respectively. The greatest inhibition zone was obtained from methanol extract against E. coli and S. aureus, both including the strong category. The LC50 value of methanol extract and methanol fraction was 273.57 µg/ml and 765.66 µg/ml, respectively, categorized as toxic against Artemia salina, while ethyl acetate fraction was not toxic.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2023 Zakaria Zakaria, Misriyani Misriyani, Ayun Dwi Astuti, Ayu Masyita

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Copyright on any article is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal, the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





_copy1.png)










