NEW PRIMER DESIGN of MULTIPLEX POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR) for DETECTION of Escherichia Coli and Salmonella Enterica in FOOD SAMPLE
Abstract
Background: Multiplex PCR techniques are used to detect multiple pathogens at the same time simultaneously. In order to achieve the specificity and sensitivity of detection, it is important to optimize the multiplex PCR method properly. Developing suitable primers and optimizing PCR temperature to boost particular genes from pathogens are key factors for this optimization.
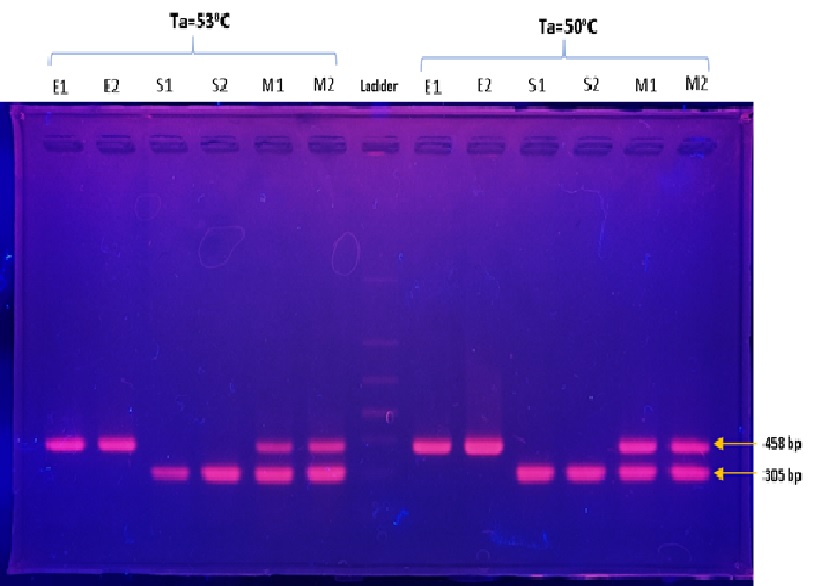
Methods: For the simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica in food samples, this research aims to develop a set of primers for multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Using Primer-BLAST software, the study utilizes specific primer designs for the phoA gene (Eschericia coli) and invA gene (Salmonella enterica). DNA isolation has confirmed successful extraction from the two bacterial samples. PCR was performed under different conditions, including Singleplex and Multiplex PCR, using two annealing temperatures of 53oC and 50oC.
Results: The results showed that this method can effectively amplify target genes and indicate their specificity and reliability at both temperature levels. Given these results, it has successfully conducted multiplex PCR using the built primer pairs. Both annealing temperatures of 50oC and 53oC can be used to perform multiplex PCR to detect E. coli and Salmonella enterica in one PCR reaction.
Conclusion: Through this research, we have created a new set of Multiplex PCR Primers and an optimized multiplex PCR technique for the simultaneous detection of E coli and Salmonella enterica in food samples. The rapid and simultaneous screening of E. coli and S. enterica, which contributes to improved food safety measures and pathogen detection in the food industry, is promising with this optimized PCR approach.
Downloads
References
Al-Jobori, K., & Nader, M. (2016). Detection of E.coli, Salmonella spp., and Listeria Monocytogenes in Retail Chicken Meat and Chicken Giblets Samples Using Multiplex PCR in Baghdad City Production of antibacterial agent from Streptomyces griseus by using Semi Solid Fermentation View project Molecular Biology View project. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences 5(9): 290-301. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.509.033
Ch en, Y., Wang, Z., Shi, Q., Huang, S., Yu, T., Zhang, L., & Yang, H. (2021). Multiplex PCR method for simultaneous detection of five pathogenic bacteria closely related to foodborne diseases. Biotech, 11(5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02759-y
Delbeke, S., Ceuppens, S., Holvoet, K., Samuels, E., Sampers, I., & Uyttendaele, M. (2015). Multiplex real-time PCR and culture methods for detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and Salmonella Thompson in strawberries, a lettuce mix and basil. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 193, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJFOODMICRO.2014.10.009.
Hernández Hernández, O., Gutiérrez-Escolano, A. L., Cancio-Lonches, C., Iturriaga, M. H., Pacheco-Aguilar, J. R., Morales-Rayas, R., & Arvizu-Medrano, S. M. (2022). Multiplex PCR method for the detection of human norovirus, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., and shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli in blackberry, coriander, lettuce and strawberry. Food Microbiology, 102,103926.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FM.2021.103926
Ip, S. C. Y., Lin, S. wah, & Lai, K. ming. (2015). An evaluation of the performance of five extraction methods: Chelex® 100, QIAamp® DNA Blood Mini Kit, QIAamp® DNA Investigator Kit, QIAsymphony® DNA Investigator® Kit and DNA IQTM. Science & Justice, 55(3), 200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCIJUS.2015.01.005
Lindsey, R. L., Garcia-Toledo, L., Fasulo, D., Gladney, L. M., & Strockbine, N. (2017). Multiplex polymerase chain reaction for identification of Escherichia coli, Escherichia albertii and Escherichia fergusonii. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 140, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MIMET.2017.06.005
Ludwig, J. B., Shi, X., Shridhar, P. B., Roberts, E. L., DebRoy, C., Phebus, R. K., Bai, J., & Nagaraja, T. G. (2020). Multiplex PCR Assays for the Detection of One Hundred and Thirty Seven Serogroups of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Associated With Cattle. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00378
Molina, F., López-Acedo, E., Tabla, R., Roa, I., Gómez, A., & Rebollo, J. E. (2015). Improved detection of Escherichia coli and coliform bacteria by multiplex PCR. BMC Biotechnology, 15(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12896-015-0168-2/FIGURES/2
Nguyen, T. T., Van Giau, V., & Vo, T. K. (2016). Multiplex PCR for simultaneous identification of E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp. and L. monocytogenes in food. 3 Biotech, 6(2), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205016-0523-6/FIGURES/4
Sahu, B., Singh, S. D., Behera, B. K., Panda, S. K., Das, A., & Parida, P. K. (2019). Rapid detection of Salmonella contamination in seafoods using multiplex PCR. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 50(3), 807–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42770019-00072-8/METRICS
Sint, D., Raso, L., & Traugott, M. (2012). Advances in multiplex PCR: balancing primer efficiencies and improving detection success. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3(5),898.https://doi.org/10.1111/J.204-210X.2012.00215.X
Tao, J., Liu, W., Ding, W., Han, R., Shen, Q., Xia, Y., Zhang, Y., & Sun, W. (2020). A multiplex PCR assay with a common primer for the detection of eleven foodborne pathogens. Journal of Food Science, 85(3), 744754.https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15033
Wei, C., Zhong, J., Hu, T., & Zhao, X. (2018). Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella by multiplex PCR in milk. 3 Biotech, 8(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-018-1086-5/METRICS
Wei, S., Daliri, E. B. M., Chelliah, R., Park, B. J., Lim, J. S., Baek, M. A., Nam, Y. S., Seo, K. H., Jin, Y. G., & Oh, D. H. (2019). Development of a multiplex real-time PCR for simultaneous detection of Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus in food samples. Journal of Food Safety, 39(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12558
Xu, M., Wang, R., & Li, Y. (2016). Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium in foods using an electrochemical immunosensor based on screen-printed interdigitated microelectrode and immunomagnetic separation. Talanta, 148, 200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2015.10.082
Copyright (c) 2024 Muhammad Taufiq Hidayat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this Journal agree to the following terms:
- Author retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a creative commons attribution license that allow others to share the work within an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication of this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangement for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g. acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal).
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published works




 2
2






