Screening Emodin Derivatives as DPP-4 Inhibitor Candidates: In Silico and In Vitro Assessment
Abstract
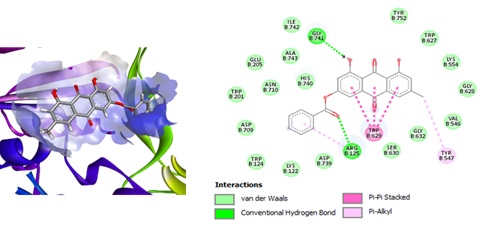
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disease distinguished by disrupted glucose metabolism, causing elevated blood sugar levels. One of the latest therapeutic strategies involves inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) to regulate glucose metabolism. Emodin, a bioactive compound, has shown potential as a DPP-4 inhibitor, but its efficacy requires further research. This study aims to identify and assess emodin and its derivatives as potential DPP-4 inhibitors through a comprehensive in silico and in vitro analysis. Molecular docking analysis revealed that 3-ρ-toluoyl emodin (ρTE) had the lowest binding energy (-111.4 kcal/mol) among the tested compounds. Furthermore, in vitro testing showed consistent results in silico, indicating that ρTE had significant inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 1.37 μM. Pharmacokinetic and physicochemical evaluations confirmed ρTE’s potential as a safe antidiabetic drug candidate. The research findings indicate that ρTE holds potential as a promising drug candidate for further development.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2025 Dina Azkiyah, Gustini Syahbirin, Firdayani Firdayani, Purwantiningsih Sugita

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Copyright on any article is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal, the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work’s authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





_copy1.png)










