LITERATURE REVIEW: METALLOTHIONEIN SEBAGAI PROTEIN PENGIKAT LOGAM UNTUK BIOREMEDIASI LOGAM BERAT
Abstract
Background: The purpose of bioremediation is to remove or reduce dangerous compounds to improve environmental quality, one of which is heavy metals. Metal-binding proteins can minimize the impact of heavy metal pollution from the environment. This metal binding protein can accumulate metals by microorganisms. One of the known metal-binding proteins is metallothioneins (MTs). This protein can minimize the effects of heavy metals in the environment by creating protein-metal ion complex bonds. This review article provides a comprehensive insight into the role of metallothionein as a metal-binding protein for heavy metal accumulation, and the mechanisms involved in heavy metal bioremediation
Methods: The method used is a literature review using reputable national and international journals.
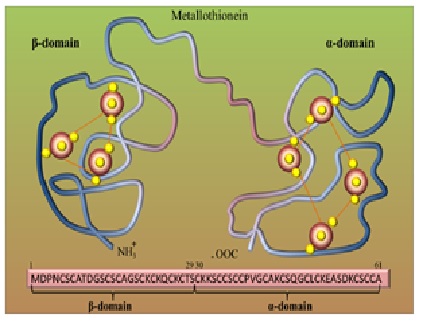
Results: Based on the results of a literature review, metallothionein can be found in many organisms such as bacteria, humans, plants, invertebrates, and mammals. Metallothionein can accumulate heavy metals that contain highly conserved cysteine residues. These residues allow MTs to bind, transport, and store various essential (Zn and Cu) and non-essential (Cd and Hg) heavy metals via thiolate bonding.
Conclusion: Heavy metals are dangerous for the survival of living things and can cause damage to vital functions. One of the metal-binding proteins is metallothionein, which is involved in the organism's tolerance to heavy metal content and can accumulate it, so that the effects of heavy metals can be minimized.
Downloads
References
Abdelmigid, H.M., 2016. Expression analysis of Type 1 and 2 Metallothionein genes in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) during short-term stress using sqRT-PCR analysis.
Ahuti, S., 2015. Industrial growth and environmental degradation. Int. Educ. Res. J. 1, 5–7. 413
Ayilara, M. S., & Babalola, O. O. (2023). Bioremediation of environmental wastes: the role of microorganisms. Frontiers in Agronomy, 5, 1183691.
Bala, S., Garg, D., Thirumalesh, B. V., Sharma, M., Sridhar, K., Inbaraj, B. S., & Tripathi, M. (2022). Recent strategies for bioremediation of emerging pollutants: a review for a green and sustainable environment. Toxics, 10(8), 484.
Balzano, S., Sardo, A., Blasio, M., Chahine, T. B., Dell’Anno, F., Sansone, C., & Brunet, C. (2020). Microalgal metallothioneins and phytochelatins and their potential use in bioremediation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 517.
Barbato, M., Mapelli, F., Crotti, E., Daffonchio, D., & Borin, S. (2019). Cultivable hydrocarbon degrading bacteria have low phylogenetic diversity but highly versatile functional potential. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 142, 43-51.
Benhalima L, Amri S, Bensouilah M, Ouzrout R (2020) Heavy metal resistance and metallothionein induction in bacteria isolated from Seybouse river Algeria. Appl Ecol Environ Res 18(1):1721–1737. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1801_17211737
Chatterjee, S., Kumari, S., Rath, S., Priyadarshanee, M., & Das, S. (2020). Diversity, structure and regulation of microbial metallothionein: Metal resistance and possible applications in sequestration of toxic metals. Metallomics, 12(11), 1637-1655.
Chaturvedi, R., & Archana, G. (2014). Cytosolic expression of synthetic phytochelatin and bacterial metallothionein genes in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 for enhanced tolerance and bioaccumulation of cadmium. Biometals, 27, 471-482.
Chen B, Fang L, Yan X, Zhang A, Chen P, Luan T, Hu L, Jiang G (2019) A unique Pb-binding fagellin as an efective remediation tool for Pb contamination in aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 363:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.004
Dash, D. M., & Osborne, W. J. (2022). A systematic review on the implementation of advanced and evolutionary biotechnological tools for efficient bioremediation of organophosphorus pesticides. Chemosphere, 137506.
De Oliveira, V. H., Ullah, I., Dunwell, J. M., & Tibbett, M. (2020). Bioremediation potential of Cd by transgenic yeast expressing a metallothionein gene from Populus trichocarpa. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 202, 110917.
Diep, P., Mahadevan, R., and Yakunin, A. F. (2018). Heavy metal removal by bioaccumulation using genetically engineered microorganisms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 6:157. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00157
Dundar, E., Sonmez, G. D., & Unver, T. (2015). Isolation, molecular characterization and functional analysis of OeMT2, an olive metallothionein with a bioremediation potential. Molecular genetics and genomics, 290, 187-199.
Geva, P., Kahta, R., Nakonechny, F., Aronov, S., & Nisnevitch, M. (2016). Increased copper bioremediation ability of new transgenic and adapted Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 19613-19625.
Gogoi, N. M., Baroowa, B., & Gogoi, N. (2021). Ecological tools for remediation of soil pollutants. In Bioremediation Science (pp. 57-78). CRC Press.
Guo S, Xiao C, Zhou N, Chi R (2021) Speciation, toxicity, microbial remediation and phytoremediation of soil chromium contamination. Environ Chem Lett 19(2):1413–1431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01114-6
He, Y., Ma, W., Li, Y., Liu, J., Jing, W., & Wang, L. (2014). Expression of metallothionein of freshwater crab (Sinopotamon henanense) in Escherichia coli enhances tolerance and accumulation of zinc, copper and cadmium. Ecotoxicology, 23, 56-64.
Hou, D., O’Connor, D., Igalavithana, A. D., Alessi, D. S., Luo, J., Tsang, D. C., ... & Ok, Y. S. (2020). Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 1(7), 366-381.
Koch, N., Islam, N. F., Sonowal, S., Prasad, R., & Sarma, H. (2021). Environmental antibiotics and resistance genes as emerging contaminants: methods of detection and bioremediation. Current research in microbial sciences, 2, 100027.
Khalid, H. S., Akhtar, M. F., Ijaz, M., Iqbal, M., Bukhari, S. A., Mustafa, G., & Shaukat, K. (2021). Role of metal-binding proteins and peptides in bioremediation of toxic metals. In Handbook of Bioremediation (pp. 437-444). Academic Press.
Krezel, A., & Maret, W. (2021). The bioinorganic chemistry of mammalian metallothioneins. Chemical Reviews, 121(23), 14594-14648.
Li, X., Ren, Z., Crabbe, M. J. C., Wang, L., & Ma, W. (2021). Genetic modifications of metallothionein enhance the tolerance and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in Escherichia coli. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 222, 112512.
Lin, K. H., Chien, M. F., Hsieh, J. L., & Huang, C. C. (2010). Mercury resistance and accumulation in Escherichia coli with cell surface expression of fish metallothionein. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 87, 561-569.
M. Megharaj, K. Venkateswarlu, R. Naidu, Bioremediation, Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), Academic Press, 2014, Pages 485-489, ISBN 9780123864550, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386454-3.01001-0.
Mudaningrat, A., Umaya, F., Syahriza, F. A. A., Anggraito, Y. U., & Setiati, N. (2023). Literature Review: LITERATURE REVIEW: APLIKASI PENANDA MOLEKULER UNTUK ANALISIS KEANEKARAGAMAN GENETIK HEWAN. BIOPENDIX: Jurnal Biologi, Pendidikan dan Terapan, 10(1), 11-25.
Sun, Q., Cheng, S. W., Cheung, K., Lee, M. M., & Chan, M. K. (2019). Cry protein crystal-immobilized metallothioneins for bioremediation of heavy metals from water. Crystals, 9(6), 287.
Thirumoorthy N, Shyam Sunder A, Manisenthil Kumar K, Senthil Kumar M, Ganesh G, Chatterjee M. A review of metallothionein isoforms and their role in pathophysiology. World J Surg Oncol. 2011. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-9-54. PMID: 21599891; PMCID: PMC3114003.
Osman, G. E., Abulreesh, H. H., Elbanna, K., Shaaban, M. R., & Ahmad, I. (2019). Recent Progress in Metal-Microbe Interactions: Prospects in Bioremediation. Journal of Pure & Applied Microbiology, 13(1).
Raghunandan, K., Kumar, A., Kumar, S., Permaul, K., and Singh, S., 2018. Production of gellangum, an exopolysaccharide, from biodiesel-derived waste glycerol by Sphingomonas spp. Biotech 8:71. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1096-3
Rahman, M. T., Haque, N., Abu Kasim, N. H., & De Ley, M. (2017). Origin, function, and fate of metallothionein in human blood. Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, Vol. 173, 41-62.
Sevak, P. I., Pushkar, B. K., & Kapadne, P. N. (2021). Lead pollution and bacterial bioremediation: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19(6), 4463-4488.
Si, M., & Lang, J. (2018). The roles of metallothioneins in carcinogenesis. Journal of hematology & oncology, 11(1), 1-20.
Sun, Q., Cheng, S. W., Cheung, K., Lee, M. M., & Chan, M. K. (2019). Cry protein crystal-immobilized metallothioneins for bioremediation of heavy metals from water. Crystals, 9(6), 287.
Tasleem, M., Hussein, W. M., El-Sayed, A. A. A., & Alrehaily, A. (2023). An In Silico Bioremediation Study to Identify Essential Residues of Metallothionein Enhancing the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms, 11(9), 2262.
Verma, S., & Kuila, A. (2019). Bioremediation of heavy metals by microbial process. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 14, 100369.
Wong, D. L., Merrifield-MacRae, M. E., & Stillman, M. J. (2017). Lead (II) binding in metallothioneins. Lead: Its Effects on Environment and Health, 17, 241.
Authors who publish with this Journal agree to the following terms:
- Author retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a creative commons attribution license that allow others to share the work within an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication of this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangement for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g. acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal).
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published works




 2
2






