ANALISIS PENGGUNAAN MODEL PEMBELAJARAN HYPOTHETICAL – DEDUCTIVE LEARNING CYCLES UNTUK MENINGKATKAN HASIL BELAJAR IPA-BIOLOGI SISWA SMP
Abstract
Background: Student learning outcomes of SMP Negeri 22 Ambon on the subject of additive biology learning have not yet fully reached the KKM because the learning process only prioritizes the completeness of the material and the learning strategies applied by the teacher still tend to use the lecture method. The Hypothetical-Deductive Learning Cycles (HDLC) learning model provides opportunities for students to construct their own knowledge and act like scientists. This study aims to determine the improvement of science-biology learning outcomes for junior high school students using the hypothetical-deductive learning cycles model of additive material in class VIII SMP Negeri 22 Ambon.
Methods: The type of research used is descriptive research which is used to determine the improvement of student learning outcomes.
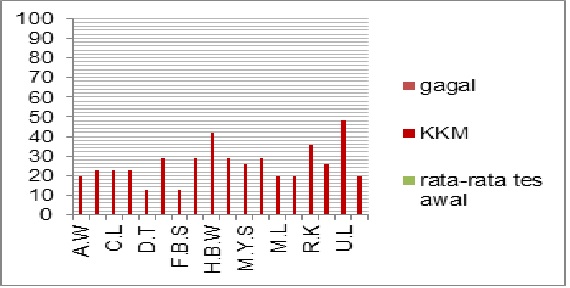
Results: The results of the study illustrate that the learning outcomes of Biology Sciences for junior high school students before the application of the hypothetical - deductive learning cycles learning model were under the KKM, but after the application of the hypothetical - deductive learning cycles model, the SMP students' learning outcomes of Biology turned out to be increased and fulfilled the KKM.
Conclusion: Based on the results of research and discussions that have been carried out, it can be concluded that the final score (NA) obtained by each student shows that using the hypothetical-deductive learning cycles model can help students improve learning outcomes.
Downloads
Authors who publish with this Journal agree to the following terms:
- Author retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a creative commons attribution license that allow others to share the work within an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication of this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangement for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g. acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal).
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published works




 2
2






