EFFECTIVENESS OF MAJA FRUIT EXTRACT (Aegle marmelos) AS AN ALTERNATIVE FOR PEST CONTROL LIVING LOCKS (Locusta migratoria)
Abstract
Background: Control of wandering grasshoppers at the farmer level generally uses chemical insecticides which can damage non-target organisms, pest resistance, pest resurgence and cause residual effects
Methods: Laboratory experimental research, although it can also be carried out outside the laboratory, its implementation applies laboratory principles.
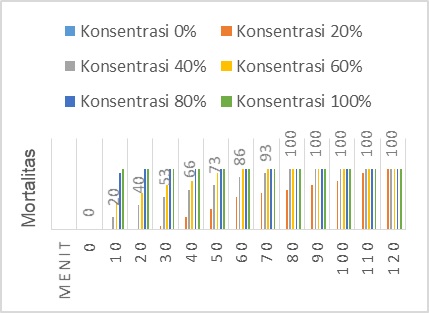
Results: The effectiveness of the mortality of maja fruit extract on wandering grasshoppers, in the treatment of giving 40% maja fruit extract, there was an increase in the number of deaths of wandering grasshoppers, where in the 10th minute there was 20% death, there had already been deaths compared to the treatment giving 20% extract with the same amount. wandering grasshoppers died by 100%.
Conclusion: Maja fruit extract (Aegle marmelos), has the power to kill wandering grasshoppers (Locusta migratoria) because it contains tannins and saponins which are toxic and have a real effect in killing wandering grasshoppers
Downloads
References
Arumugam S., Kavimani S., Kadalmani B., et al. (2008). Antidiabetic Activity Of Leaf and Callus Extracts Of Aegle marmelos in Rabbit. Science Asia, 34 : 317-321
Dhankar S., Ruhil S., Balhara M., Dhankar S and Chhillar A.K. (2011). Aegle marmelos (Linn.) Correa: A potential Source of Phytomedicine. Journal of Medicinal
Erlan Ardiana Rismansyah, wordpress.com/2010/01/07/ Pembuangan dan Pemusnahan Insektisida
Kamalakannan N and Prince P.S. (2003). Hypoglycemic of water Extracts of Aegle marmelos Fruits in Streptozotocin Diabetic Rats. J Ethnpharmacol. 87 : 207.
Kardinan, A. 2002. Pestisida Nabati. Penerbit Swadaya. Jakarta
Kesari A.n., Gupta R.K., Singh S.K., Diwakar S and Watal G. (2006). Hypoglycemic and Antihypergycemic seed extractin Normal and Diabetic Rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 107 :374.
Naresh, C., Adarsh, M., Mehta, & Dodia. (2012). Primary identification of certain phytochemical constituents of aegle marmelos (l.) Corr. Serr responsible for antimicrobial activity against selected vegetable and clinical pathogen. International Journal of Physical and Social Sciences.
Prihatman. 2001. Saponin untuk Pembasmi Hama Udang. Laporan Hasil Penelitian. Pusat Penelitian
Sabu M.C. and Kuttan R. (2004). Antidiabetic Activity of Aegle marmelos and Its Relationship With Its Antioxsidant Properties. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 48(1) :81-88.
Samsudin. 2008. Virus Patogen Serangga:Bio-Insektisida Ramah Lingkungan.
Suparjo. 2008. Saponin Peran dan Pengaruhnya Bagi Ternak dan Manusia. Fakultas Peternakan. Universitas Jambi: Jambi.
US EPA. (2002). Indoor Air and Asthma. www. Epa.gov./asthma. Diakses 20 Mei 2011.
Wijaya, K.A. 2012. Pengantar Agronomi Sayuran Jakarta: Prestasi Pustaka.
Winarno, F. G. 2002. Kimia Pangan dan Gizi. PT. Gramedia Pustaka Utama. Jakarta.
Yunita, E. A., Nanik H. S. dan Jafron W. H. (2009). “Pengaruh Ekstrak Daun Teklan (Eupatorium riparium) Terhadap Mortalitas dan Perkembangan Larva Aedes aegypti”. BIOMA. 11 (1)
Authors who publish with this Journal agree to the following terms:
- Author retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a creative commons attribution license that allow others to share the work within an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication of this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangement for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g. acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal).
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published works




 2
2






