KELIMPAHAN DAN KARAKTERISTIK BAKTERI KOLIFORM PADA BAKASANG BIA GARU (Tridacna gigas L) BERDASARKAN JENIS BAHAN PENGAWET
Abstract
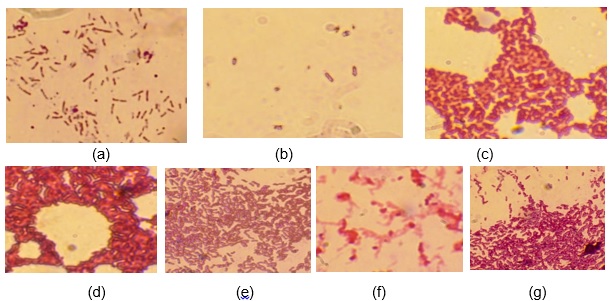
Background: Giant clam or bia garu is a kind of bivalves in the coral ecosystems. This biota is used as the raw material for processing bakasang by the people of the Babar Islands in Maluku. Preservatives used in the processing of bakasang are depend on the habits of the people. This study aims to determine the number and characteristics of coliform bacteria in clams bakasang based on the type of preservative. Methods:The presumptive test used the Most Probably Number (MPN) method on Lactose broth followed by characterization on Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMBA) media. Result: The number of coliform bacteria in clams bakasang using palmyra vinegar was 20 MPN/g while bakasang using salt and vinegar was 150 MPN/g. The macroscopic characterization of coliform bacteria in both types of clams bakasang were metallic green and pink with varying edges and elevations. In bakasang using palmyra vinegar were also found yellow and white coliform bacteria. The Microscopic characterization of coliform bacteria in clams bakasang was Gram negative rods with varied cell arrangement. Conclusion: It is suspected that these bacteria belong to the genera Citrobacter, Enterobacter, and Escherichia.
Downloads
Authors who publish with this Journal agree to the following terms:
- Author retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a creative commons attribution license that allow others to share the work within an acknowledgement of the work’s authorship and initial publication of this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangement for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal’s published version of the work (e.g. acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal).
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published works




 2
2






