GeoGebra as a Visualization Tool: Implications for Mathematics Anxiety in Analytical Geometry Lectures
Abstract
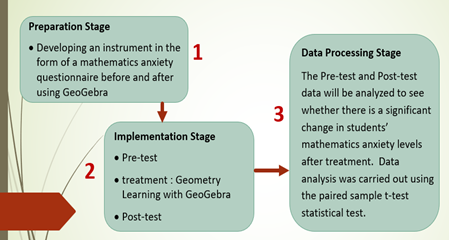
This study investigates the impact of using GeoGebra as a geometric visualization tool on reducing mathematics anxiety among students in a Mathematics Education program. GeoGebra, an interactive software, enables dynamic visualization of geometric concepts, potentially fostering deeper conceptual understanding and alleviating anxiety in learning mathematics. A one-group pretest-posttest design was employed, consisting of three phases: preparation, implementation, and data analysis. Data were collected through a mathematics anxiety questionnaire administered before and after the intervention using Google Forms. The participants were 45 Mathematics Education students enrolled in an Analytical Geometry course. Data analysis involved tests of normality, homogeneity, and a paired sample t-test. The results indicate that: (1) GeoGebra effectively reduces students' anxiety in learning geometry; (2) its interactive visualizations enhance conceptual understanding and mitigate anxiety levels; (3) there is a statistically significant difference in anxiety levels before and after the use of GeoGebra; and (4) students reported a more enjoyable and less stressful learning environment, which increased their engagement with the course content. These findings suggest that integrating GeoGebra into geometry instruction can be a valuable pedagogical strategy for reducing mathematics anxiety and promoting meaningful learning experiences
Downloads
References
Amdar, F. F., Putri, S. J. A., Nurazizah, N., & Irmayanti, I. (2024, May 9). Geometry Learning Strategy at MTs Negeri 1 Sinjai. SciSpace - Paper. https://doi.org/10.58355/competitive.v3i2.53
Anggraini, S. B., Ummam, F., Sari, M. P., & Amaliyah, F. (2024). Pengaruh Tingkat Kecemasan Matematika terhadap Hasil Tes Penalaran Matematis pada Siswa Kelas V SD 5 Mejobo. Bilangan : Jurnal Ilmiah Matematika, Kebumian Dan Angkasa, 2(4), 128–136. https://doi.org/10.62383/bilangan.v2i4.164
Ardina, G., & Boholano, H. B. (2024). The Cognitive and Non-Cognitive Effects of Geogebra Integration. Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 18(2), 423–443. https://doi.org/10.47836/mjms.18.2.12
Atoyebi, O. M., & Atoyebi, S. B. (2022). Do Technology-based Approaches Reduce Mathematics Anxiety? A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science, 06(10), 502–509. https://doi.org/10.47772/ijriss.2022.61027
Azizah, F. N., Waluya, B., & Masduki, L. R. (2023). Analisis Kemampuan Literasi Matematik Melalui Think-Talk-Write (Ttw) Berbantuan Geogebra Ditinjau Dari Self Efficacy Peserta Didik Kelas VI. Syntax Literate ; Jurnal Ilmiah Indonesia, 8(2), 1080–1094. https://doi.org/10.36418/syntax-literate.v8i2.11372
Banu, S. S. (2024, March 6). Exploring geogebra: An interactive tool for mathematical visualization and analysis. SciSpace - Paper. https://doi.org/10.58532/v3bjcm1p1ch3
Chadwick, D. (2024). Providing working memory support to anxious students using cognitive load theory compliant instructions.
Chakrabartty, S. N. (2020). Discriminating Value of Item and Test. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 59(3), 61–78.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed). L. Erlbaum Associates.
Cotabish, A., Dailey, D., Trumble, J., & Miller, R. (2024, July 1). Spatial Reasoning Excellence: A Synergy of VanTassel-Baska’s Integrated Curriculum Model and Talent Development (2024) | Alicia Cotabish | 1 Citations. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14070716
Davison, G. C. (2015). Bandura, Albert (b. 1925). In The Encyclopedia of Clinical Psychology (pp. 1–3). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118625392.wbecp430
Dowker, A., Sarkar, A., & Looi, C. Y. (2016). Mathematics Anxiety: What Have We Learned in 60 Years? Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 508. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00508
Em, A. M. M., & Roman, A. G. (2020). Effectiveness of GeoGebra in Teaching Grade 10 Mathematics. 3(2).
Farhan, M., & Yahfizham, Y. (2023). Analisis Penggunaan Algoritma Pemrograman dan Aplikasi Geogebra dalam Pembelajaran Matematika Geometri. Jurnal Arjuna, 1(6), 76–90. https://doi.org/10.61132/arjuna.v1i6.295
Gale, J., Alemdar, M., Cappelli, C., & Morris, D. (2021). A Mixed Methods Study of Self-Efficacy, the Sources of Self-Efficacy, and Teaching Experience. Frontiers in Education, 6, 750599. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2021.750599
Gill, G. K. (2018, November). Prevalence of Mathematics Anxiety in Preservice Teachers and Preservice Counselors. Oregon State University.
Handayani, S., & Permatasari, D. N. (2022). Analysis of students’ anxiety based on Van Hiele’s levels in solving geometry problems. Beta: Jurnal Tadris Matematika, 15(2), 135–150. https://doi.org/10.20414/betajtm.v15i2.551
Hohenwarter, M., & Lavicza, Z. (2009). The strength of the community: How GeoGebra can inspire technology integration in mathematics teaching. MSOR Connections, 9(2), 3–5. https://doi.org/10.11120/msor.2009.09020003
Ingram, N., Hatisaru, H., Grootenboer, P., & Beswick, K. (2020, January 1). Researching the Affective Domain in Mathematics Education. SciSpace - Paper; Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4269-5_7
Isa, N. F. M., & Johari, K. S. K. (2023). Exploring Learning Motivation and Anxiety among Secondary School Students. International Journal of Academic Research in Business & Social Sciences. https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarbss/v13-i12/20273
Kongkaew, C., Scholfield, C. N., Supapaan, T., Mann, C., Mongkhon, P., & Chanunun, S. (2020, January 8). Impact of research-based learning on student knowledge and assessment in Pharmacoepidemiology: A one group pretest-posttest experimental study. SciSpace - Paper.
Lavicza, Z., Abar, C. A. A. P., & Tejera, M. (2023). Spatial geometric thinking and its articulation with the visualization and manipulation of objects in 3D. Educação Matemática Pesquisa. https://doi.org/10.23925/1983-3156.2023v25i2p258-277
Listiani, T., Sugiman, S., Saragih, M. J., & Chong, S. T. (2024). The Use of GeoGebra in Teaching Analytical Geometry. INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF MULTIDISCIPLINARY SCOPE, 05(03), 652–660. https://doi.org/10.47857/irjms.2024.v05i03.0790
Lübeck, M. (2023). Geometry in the Curriculum Pedagogical Projects of Mathematics Degree Courses at Parana State Universities. Acta Scientiae, 24(8), 232–257. https://doi.org/10.17648/acta.scientiae.7134
Maf’ulah, S., & Fadhilah, F. (2024). Pengaruh Kecemasan Matematika terhadap Prestasi Belajar Matematika Siswa SMP Negeri 2 Jogoroto. Postulat : Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Matematika, 5(2), 167–176. https://doi.org/10.30587/postulat.v5i2.9092
Maghfiroh, N. H., Hanurawan, F., & Hitipeuw, I. (2024). The Relationship Between Math Learning Anxiety, Time Management Ability, and Emotional Support with Academic Achievement of Junior High School Students in Indonesia. West Science Interdisciplinary Studies, 2(12), 2502–2513. https://doi.org/10.58812/wsis.v2i12.1551
Maghfiroh, R., Setiawan, A., Saputra, A. A., Afifah, A., & Darmayanti, R. (2023, July 1). MOVEON: Motivation, anxiety, and their relationship to mathematics learning outcomes. SciSpace - Paper. https://doi.org/10.51773/ajeb.v3i2.271
Martinez, A. R. (2017). The Effects of Using GeoGebra on Student Achievement in Secondary Mathematics.
Melo, A. F. de, & Leal, D. A. (2024). Affectivity in mathematics teaching: Using playfulness to combat resistance to new practices in the context of basic education. Concilium, 24(14), 295–309. https://doi.org/10.53660/clm-3759-23p27
Melo, E. V. de, Castro, D. M. de S., & Barbosa, J. A. (2024). Ensino-aprendizagem matemática no Ensino Médio e sua relação com a afetividade. Revista de Ciência e Inovação Do IF Farroupilha, 10(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.26669/2448-4091.2024.443
Megreya, A. M., Al-Emadi, A. A., Al-Ahmadi, A. M., Moustafa, A. A., & Szűcs, D. (2024). A large-scale study on the prevalence of math anxiety in Qatar. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 94(2), 539–556. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12662
Min, K. J., Jackman, J., & Zhao, Z. (2024, February 6). Work in Progress: Visual Learning and Teaching Aids for Abstract Concepts in Inventory Control towards Better Learning Outcomes. SciSpace - Paper. https://doi.org/10.18260/1-2--41092
Mijanović, N. (2023). Constructivism as a contemporary teaching paradigm. Inovacije u nastavi, 36(1), 21–32. https://doi.org/10.5937/inovacije2301021M
Mudhefi, F., Mabotja, K., & Muthelo, D. (2024). The use of Van Hiele’s geometric thinking model to interpret Grade 12 learners’ learning difficulties in Euclidean Geometry. Perspectives in Education, 42(2), 162–175. https://doi.org/10.38140/pie.v42i2.8350
Narh-Kert, M., & Sabtiwu, R. (2022). Use of GeoGebra to Improve Performance in Geometry. African Journal of Educational Studies in Mathematics and Sciences, 18(1), 29–36. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajesms.v18i1.3
Pentang, J. T., Azucena, L. J., Gacayan, P. J., Tabat, M. A., & Cuanan, K. H. (2022, November 20). Geogebra intervention: How have students’ performance and confidence in algebra advanced? SciSpace - Paper. https://doi.org/10.55687/ste.v1i1.17
Pinheiro, E. (2009). Auto-eficácia académica. ISSN: 0214-9877. pp: 331-336.
Putri, H. E., Wahyudy, M. A., Yuliyanto, A., & Nuraeni, F. (2020). Development of Instruments to Measure Mathematical Anxiety of Elementary School Students. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 19(6), 282–302. https://doi.org/10.26803/IJLTER.19.6.17
Raisatunnisa, Suryadi, D., Fatimah, S., Priatna, N., & Nasir, N. (2025). Enhancing Mathematical Literacy Through Geogebra Classroom-Assisted Learning: A Case Study in Indonesian Secondary Schools. Matematika dan pembelajaran, 13(1), 64–84. https://doi.org/10.33477/mp.v13i1.8938
Ramirez, G., Shaw, S. T., & Maloney, E. A. (2018). Math Anxiety: Past Research, Promising Interventions, and a New Interpretation Framework. Educational Psychologist, 53(3), 145–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2018.1447384
Raykov, T., Anthony, J. C., & Menold, N. (2022). On the Importance of Coefficient Alpha for Measurement Research: Loading Equality Is Not Necessary for Alpha’s Utility as a Scale Reliability Index. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 83(4), 766–781. https://doi.org/10.1177/00131644221104972
Salami, O. O., & Spangenberg, E. D. (2024). Integration of Geogebra Software Into Mathematics Instruction. Studies in Learning and Teaching, 5(1), 118–126. https://doi.org/10.46627/silet.v5i1.343
Salsanabila, M. F., Lestari, D. E., & Sari, D. Y. (2024). Geogebra As A 21st Century Learning Tool: A Systematic Literature Review. Jurnal Ilmiah Profesi Pendidikan, 9(2), 989–996. https://doi.org/10.29303/jipp.v9i2.2191
Samosir, C. M., & Dasari, D. (2022). The Effect of Math Anxiety On Mathematical Problem-Solving Ability. Tunas: Jurnal Pendidikan Guru Sekolah Dasar. https://doi.org/10.33084/tunas.v8i1.4305
Santiago, E. (2024, July 2). The teaching of trigonometry using the Geogebra software as a teaching—Learning tool. SciSpace - Paper; Seven Editora. https://doi.org/10.56238/sevened2024.013-011
Sari, A. D. Y. P., & Mujazi. (2024). Pengaruh Kecemasan Belajar Matematis Terhadap Kemampuan Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Siswa Kelas 5 SDN Setia Asih. caXra: Jurnal Pendidikan Sekolah Dasar, 4(2), 174–180. https://doi.org/10.31980/caxra.v4i2.2407
Schmid, A., Koreňová, L., Cahyono, A. N., Hvorecký, J., & Lavicza, Z. (2023). Geogebra as a Constructivism Teaching Tool for Visualization Geometry Using VR and AR. E-Learning, 253–264. https://doi.org/10.34916/el.2023.15.20
Setiawi, A. P., Suparta, I. N., & Suharta, I. G. P. (2021). The Effect of The Geogebra-Assisted Problem Based Learning Model on Problem Solving Ability and Critical Thinking Ability for Class X Students of SMA Negeri I Petang. 9(1)
Silveira, A. P. R. (2018). O GeoGebra como ferramenta de apoio para aprendizagem significativa da Geometria. Revista do Instituto GeoGebra Internacional de São Paulo, 7(1), 07–30.
Stratton, S. J. (2019). Quasi-Experimental Design (Pre-Test and Post-Test Studies) in Prehospital and Disaster Research. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine, 34(6), 573–574. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X19005053
Sunardi, S., Yudianto, E., Susanto, S., Kurniati, D., Cahyo, R. D., & Subanji, S. (2019). Anxiety of Students in Visualization, Analysis, and Informal Deduction Levels to Solve Geometry Problems. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 18(4), 171–185. https://doi.org/10.26803/IJLTER.18.4.10
Thi Thu, H. L., & Thi Thu, H. T. (2023). APPLYING CONSTRUCTIVIST THEORY IN TEACHING MATHEMATICS AT GRADE 2. International Journal of Education and Social Science Research, 06(02), 213–220. https://doi.org/10.37500/IJESSR.2023.6219
Thom, J. S., McGarvey, L. M., & Markle, J. (2024). Projective geometry and spatial reasoning for STEM learning. Frontiers in Education. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1312845
Wahyuni, R., Juniati, D., & Wijayanti, P. (2024). How do Math Anxiety and Self-Confidence Affect Mathematical Problem Solving? TEM Journal. https://doi.org/10.18421/tem131-58
Zakelj, A., & Klančar, A. (2022). The Role of Visual Representations in Geometry Learning. European Journal of Educational Research, 11(3), 1393–1411. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.11.3.1393
Zetriuslita, Z., Nofriyandi, N., & Istikomah, E. (2020). The Effect Of Geogebra-Assisted Direct Instruction On Students’ Self-Efficacy and Self-Regulation. Infinity Journal, 9(1), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v9i1.p41-48
Ziatdinov, R., & Valles, J. R. (2022). Synthesis of Modeling, Visualization, and Programming in GeoGebra as an Effective Approach for Teaching and Learning STEM Topics. Mathematics, 10(3), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10030398
Copyright (c) 2025 Maria Martini Aba, Yus Mochamad Cholily, Baiduri Baiduri, Siti Inganah, Zainur Wula, Abdulkadir Rahardjanto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
License and Copyright Agreement
By submitting a manuscript to Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (JUPITEK), the author(s) certify and agree to the following terms:
- Originality and Authority: The submitting author is authorized by all co-authors to enter into this agreement. The manuscript describes original work that has not been published previously in a peer-reviewed journal, nor is it under consideration for publication elsewhere.
- Approval: Its publication has been approved by all author(s) and by the responsible authorities of the institutions where the work was carried out.
- Rights: The authors secure the right to reproduce any material that has already been published or copyrighted elsewhere.
- Licensing and Copyright: Authors retain the copyright to their work.
- License Grant: The authors grant Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (JUPITEK) the right of first publication, with the work simultaneously licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).
- Self-Archiving: Authors are permitted and encouraged to deposit the published version of their article in institutional repositories, on their personal websites, and other academic platforms, with proper acknowledgment of its initial publication in Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (JUPITEK).





.png)


