PENGARUH COGNITIVE SKILLS TERHADAP HASIL BELAJAR MATEMATIKA SECARA DARING
Abstract
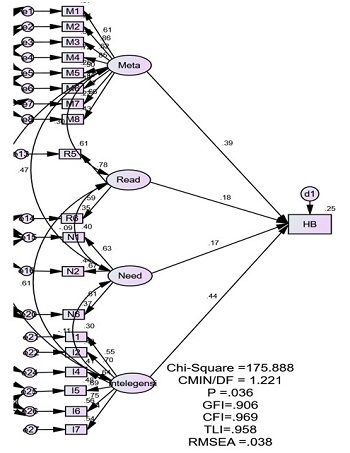
The covid 19 pandemic that occurred resulted in the learning process being carried out online, but online learning was found to have many obstacles so that in order to make online learning effective, students' cognitive abilities must be optimized. This quantitative study aims to analyze the cognitive skills of students that can influence online mathematics learning outcomes and to describe the cognitive skills variables that have the dominant influence. This research is a quantitative survey research conducted in January-March 2021 involving 155 high school students in Makassar City, consisting of 95 women and 60 men. The research variables consisted of exogenous variables, namely cognitive skills (metacognition, reading comprehension ability, cognitive needs, and intelligence), while the endogenous variables were the results of learning mathematics. The instruments used to measure exogenous variables are questionnaires and intelligence tests that meet the validity and reliability tests. The endogenous variable is learning outcomes obtained from the documentation value of students' mathematics learning outcomes (report scores). The data was processed by descriptive analysis and inferential analysis using structural equation modeling (SEM). The results of the study indicate that metacognition and intelligence have a positive and significant effect on online mathematics learning outcomes, it means that the higher the metacognition and intelligence possessed by students, the student's learning outcomes will increase. Meanwhile, reading comprehension skills and cognitive needs were found to have no significant effect on online mathematics learning outcomes, this means that reading comprehension skills and cognitive needs have not provided sufficient evidence that they can affect online mathematics learning outcomes. The cognitive skills variable that gives the dominant influence on online mathematics learning outcomes is intelligence with a contribution of 19.53%. This shows that intelligence has a great influence on the online learning process of mathematics
Downloads
References
Adinda, P. (2020). Sistem Pendidikan Sedunia Terdampak Corona, PBB: Malapetaka Generasi di Depan Mata. https://asumsi.co/post/sistem-pendidikan-sedunia-terdampak-corona-pbb-malapetaka-generasi-di-depan-mata
Adiwisastra, M. F., & Basjaruddin, N. C. (2017). Intelligent Tutoring System Untuk Mengukur Kemampuan Kognitif Dalam Fisika Dasar Berbasis Metode Bayesian Network. IJCIT (Indonesian Journal on Computer and Information Technology), 2(2), 40-47.
Almaiah, M. A., Al-Khasawneh, A., & Althunibat, A. (2020). Exploring the critical challenges and factors influencing the E-learning system usage during COVID-19 pandemic. Education and information technologies, 25(6), 5261-5280
Amindoni, A. (2020). Virus corona: Gelombang PHK di tengah pandemi Covid-19. https://www.bbc.com/indonesia/indonesia-52218475
Amir, M. F., & Kurniawan, M. I. (2020). Penerapan pengajaran terbalik untuk meningkatkan hasil belajar mahasiswa PGSD UMSIDA pada materi pertidaksamaan linier. PEDAGOGIA: Jurnal Pendidikan, 5(1), 13-26
Arriah, F. (2016). Pengaruh Metakognisi dan Efikasi Diri Terhadap Prestasi Belajar Matematika melalui Kreativitas Belajar Siswa Kelas XI SMA Negeri Di Kota Kabupaten Bulukumba (Doctoral dissertation, Pascasarjana).
Assari, S. A. (2013). Pengaruh Kemampuan Membaca Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Ditinjau Dari Jenis Kelamin Siswa Kelas Vii Semester Genap Smp Negeri 1 Sambi Tahun Ajaran 2012/2013 (Doctoral dissertation, Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta).
Astini, N. K. S. (2020). Pemanfaatan teknologi informasi dalam pembelajaran tingkat sekolah dasar pada masa pandemi covid-19. Lampuhyang, 11(2), 13-25.
Astuti, D. D., Waluya, B., & Soedjoko, E. (2020). Mathematical representation ability and curiosity of 8th graders in the 7E-Learning Cycle Model with realistic approaches. Unnes Journal of Mathematics Education, 9(2), 116-120
Azlan, C. A., Wong, J. H. D., Tan, L. K., Muhammad Shahrun, M. S. N., Ung, N. M., Pallath, V., Tan, C. P. L., Yeong, C. H., & Ng, K. H. (2020). Teaching and learning of postgraduate medical physics using Internet-based e-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic – A case study from Malaysia. Physica Medica, 80, 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.10.002
Azubuike, O. B., Adegboye, O., & Quadri, H. (2021). Who gets to learn in a pandemic? Exploring the digital divide in remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 2, 100022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2020.100022
Baber, H. (2021). Modelling the acceptance of e-learning during the pandemic of COVID-19-A study of South Korea. International Journal of Management Education, 19(2), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2021.100503
Bakar, M. A. A., & Ismail, N. (2020). Express students’ problem solving skills from metacognitive skills perspective on effective mathematics learning. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(4), 1404–1412. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.080433
Barak, M., & Levenberg, A. (2016). Flexible thinking in learning: An individual differences measure for learning in technology-enhanced environments. Computers and Education, 99, 39–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.04.003
Basri, H. (2018). Kemampuan kognitif dalam meningkatkan efektivitas pembelajaran ilmu sosial bagi siswa sekolah dasar. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan, 18(1), 1–9.
Batubara, H. H., & Batubara, D. S. (2020). Penggunaan Video Tutorial Untuk Mendukung Pembelajaran Daring Di Masa Pandemi Virus Corona. Muallimuna : Jurnal Madrasah Ibtidaiyah, 5(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.31602/muallimuna.v5i2.2950
Belawati, T. (2020). Buku Pembelajaran Daring. Universitas Terbuka.
Biggs, J. (1988). The role of metacognition in enhancing learning. Australian Journal of education, 32(2), 127-138
Cazan, A. M., & Indreica, S. E. (2014). Need for cognition and approaches to learning among university students. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 127, 134-138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.03.227
Dabarera, C., Renandya, W. A., & Zhang, L. J. (2014). The impact of metacognitive scaffolding and monitoring on reading comprehension. System, 42, 462-473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2013.12.020
Daniel, S. J. (2020). Education and the COVID-19 pandemic. Prospects, 49(1–2), 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-020-09464-3
Dewi, R. K., Rosidin, U., & Nyeneng, I. D. P. (2013). Pengaruh Keterampilan Metakognisi Terhadap Keterampilan Berkomunikasi Dan Keterampilan Berpikir Kritis. Jurnal Pembelajaran Fisika, 1(1), 35–44.
Dimyati, M. (2006). Belajar dan Pembelajaran. Rineka Cipta.
Duru, A., & Koklu, O. (2011). Middle school students’ reading comprehension of mathematical texts and algebraic equations. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 42(4), 447–468. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2010.550938
Dwi, B., Amelia, A., Hasanah, U., Putra, A. M., & Rahman, H. (2020). Peningkatan Efektivitas Pada Proses Pembelajaran. Jurnal Pendidikan Guru SD, 2(1), 28–37.
Ehrlich, H., McKenney, M., & Elkbuli, A. (2020). We Asked the Experts: Virtual Learning in Surgical Education During the COVID-19 Pandemic-Shaping the Future of Surgical Education and Training. World Journal of Surgery, 44(7), 2053–2055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-020-05574-3
Eilifsen, Messier, Glover, & Prawitt. (2014). Auditing & Assurance Services.
Elias, S. M., & Loomis, R. J. (2002). Utilizing need for cognition and perceived self-efficacy to predict academic performance. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 32(8), 1687–1702. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2002.tb02770.x
Fajar, M. (2017). Peranan Intelegensi Terhadap Perkembangan Keterampilan Fisik Motorik Peserta Didik Dalam Pendidikan Jasmani. Multilateral Jurnal Pendidikan Jasmani Dan Olahraga, 16(1), 58–66. https://doi.org/10.20527/multilateral.v16i1.3664
Fitrianti, I., Handayani, D. E., & Suyitno. (2020). Keefektifan Media Magic Box Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Materi Jaring-Jaring Bangun Ruang Sederhana. Mimbar PGSD Undiksha, 8(2), 323–329.
Fitrih, D. M., Ardiana, N., & Pratiwi, Y. (2018). Analisis Keterampilan Metakognitif Ditinjau Dari Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Siswa Kelas Xi Man Panyabungan. Jurnal MathEdu, 1(1), 43–52.
Fortier, A., & Burkell, J. (2014). Influence of need for cognition and need for cognitive closure on three information behavior orientations. Proceedings of the ASIST Annual Meeting, 51(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/meet.2014.14505101066
Gomez, A. L., Pecina, E. D., Villanueva, S. A., & Huber, T. (2020). The undeniable relationship between reading comprehension and mathematics performance. Issues in Educational Research, 30(4), 1329–1354.
Guven, B., & Cabakcor, B. O. (2013). Factors influencing mathematical problem-solving achievement of seventh grade Turkish students. Learning and Individual Differences, 23(1), 131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2012.10.003
Handayani, L. (2020). Keuntungan, Kendala dan Solusi Pembelajaran Daring Selama Pandemi Covid-19 : Studi Ekploratif di SMPN 3 Bae Kudus Lina Handayani. Journal Industrial Engineering & Management Research, 1(2), 16. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.7777/jiemar.v1i2.36
Haqien, D., & Rahman, A. A. (2020). Pemanfaatan Zoom Meeting untuk Proses Pembelajaran pada Masa Pandemi Covid-19. SAP (Susunan Artikel Pendidikan), 5(1). https://doi.org/10.30998/sap.v5i1.6511
Haryati, E. R. (2016). Hubungan Intelegensi dan Kemampuan Numerik dengan Prestasi Belajar Matematika Siswa Kelas V SD/MI se-Kecamatan Klirong Kabupaten Kebumen Tahun Pelajaran 2015/2016 (Doctoral dissertation, Pendidikan Matematika-FKIP).
Hasanah, A. R. (2021). Pengaruh Metakognisi, Kecerdasan Logis Matematis Dan Disposisis Matematis Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa Kelas X Sma Negeri Di Kecamatan Somba Opu (Doctoral dissertation, Universitas Negeri Makassar).
Sapri, H. A. (2019). THE INFLUENCE OF INTELLIGENCE, MOTIVATION, AND CLASS CLIMATE ON MATHEMATICS LEARNING OUTCOMES OF GRADE XII IPA STUDENTS AT SMAN 7 WAJO (Doctoral dissertation, Pascasarjana).
Imam, O. A., Mastura, M. A., & Jamil, H. (2013). Correlation between Reading Comprehension Skills and Students’ Performance in Mathematics. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 2(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v2i1.1803
Izzaty, R. E., Ayriza, Y., Setiawati, F. A., & Amalia, R. N. (2017). Prediktor Prestasi Belajar Siswa Kelas 1 Sekolah Dasar. Jurnal Psikologi, 44(2), 153. https://doi.org/10.22146/jpsi.27454
Jainuri, M. (2015). Pengaruh Sikap dan Tingkat Intelegensi terhadap Prestasi belajar Siswa Kelas II SMK Tri Bhakti Bangko.
Jati, S. N., & Diana, D. (2019). Hubungan Perilaku Social Loafing dan Need for Cognition dalam Kegiatan Kerja Kelompok pada Mahasiswa PGPAUD (Studi Identifikasi Model Pembelajaran). Eksistensi, 1(2), 67–77.
Kahfi, A. (2020). Tantangan dan Harapan Pembelajaran Jarak Jauh Di Masa Pandemi Covid 19. Dirasah, 03(2), 137–154.
Karakelle, S. (2012). Interrelations between Metacognitive Awareness, Perceived Problem Solving, Intelligence and Need for Cognition. Education and Science, 37(164), 164.
Kemendikbud. (2020). Pedoman Penyelenggaraan Belajar dari Rumah dalam Masa Darurat Penyebaran Corona Virus (Covid-19).
Lailiyah, S., Hayat, S., Urifah, S., & Setyawati, M. (2021). Levels of students’ mathematics anxieties and the impacts on Daring mathematics learning. Cakrawala Pendidikan, 40(1), 107–119. https://doi.org/10.21831/cp.v40i1.36437
Lins de Holanda Coelho, G., H. P. Hanel, P., & J. Wolf, L. (2020). The Very Efficient Assessment of Need for Cognition: Developing a Six-Item Version. Assessment, 27(8), 1870–1885. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191118793208
Lubis, A. (2018). ICT integration in 21st-century Indonesian English language teaching: Myths and realities. Cakrawala Pendidikan, 1(1).
Masliani, S. (2018). Peningkatan Intelegensi Dan Hasil Belajar Siswa Melalui Pembelajaran Fungsi Logaritma Menggunakan Model Quantum Learning. MaPan: Jurnal Matematika Dan Pembelajaran, 6(1), 70–81. https://doi.org/10.24252/mapan.2018v6n1a7
Mikus, K., Tieben, N., & Schober, P. S. (2021). Concerted cultivation in early childhood and social inequalities in cognitive skills: Evidence from a German panel study. Research in Social Stratification and Mobility, 72(September), 100547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rssm.2020.100547
Muamar, M., & Rahmi, R. (2017). Analisis Keterampilan Proses Sains Dan Keterampilan Kognitif Siswa Melalui Metode Praktikum Biologi Pada Sub Materi Schizophyta Dan Thallophyta. Jurnal Pendidikan Almuslim, 5(1), 116954.
Muloke, I., Ismanto, A., & Bataha, Y. (2017). Pengaruh Alat Permainan Edukatif (Puzzle) Terhadap Perkembangan Kognitif Anak Usia 5-6 Tahun Di Desa Linawan Kecamatan Pinolosian Kabupaten Bolaang Mongondow Selatan. Jurnal Keperawatan UNSRAT, 5(1), 111977.
Napitupulu, R. M. (2020). Dampak pandemi Covid-19 terhadap kepuasan pembelajaran jarak jauh. Jurnal Inovasi Teknologi Pendidikan, 7(1), 23–33. https://doi.org/10.21831/jitp.v7i1.32771
Neigel, A. R., Behairy, S., & Szalma, J. L. (2017). Need for cognition and motivation differentially contribute to student performance. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 16(2), 144–156. https://doi.org/10.1891/1945-8959.16.2.144
Nirfayanti, & S, E. (2021). Pengaruh Kemampuan Metakognisi Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa SMA Effect of Metacognition Skills on Mathematics Learning Outcomes of High School Students. Mathline: Jurnal Matematika Dan Pendidikan Matematika, 6(1), 109–124.
Nor, N. A. K. M., Ismail, Z., & Yusof, Y. M. (2016). The relationship between emotional intelligence and mathematical competency among secondary school students. Journal on Mathematics Education, 7(2), 91–100. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.7.2.3534.91-100
Nuere, S., & de Miguel, L. (2020). The Digital/Technological Connection with COVID-19: An Unprecedented Challenge in University Teaching. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-020-09454-6
Nurazizah, S., Sinaga, P., & Jauhari, A. (2017). Profil Kemampuan Kognitif dan Keterampilan Berpikir Kritis Siswa SMA pada Materi Usaha dan Energi. Jurnal Penelitian & Pengembangan Pendidikan Fisika, 3(2), 197–202. https://doi.org/10.21009/1.03211
OECD. (2018). PISA 2018 Results in Focu. Columbia University.
Ozturk, M., Akkan, Y., & Kaplan, A. (2020). Reading comprehension, Mathematics self-efficacy perception, and Mathematics attitude as correlates of students’ non-routine Mathematics problem-solving skills in Turkey. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 51(7), 1042–1058. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2019.1648893
Petty, R. E., Brinol, P., Loersch, C., & McCaslin, M. J. (2009). Chapter 21. The Need for Cognition. In Handbook of Individual Differences in Social Behavior. (pp. 318–329).
Purwanto, A., Pramono, R., Asbari, M., Hyun, C. C., Wijayanti, L. M., Putri, R. S., & Santoso, priyono B. (2020). Studi Eksploratif Dampak Pandemi COVID-19 Terhadap Proses Pembelajaran Daring di Sekolah Dasar. EduPsyCouns: Journal of Education, Psychology and Counseling, 2(1), 1–12.
Purwanto, N. (2012). Prinsip-Prinsip dan Teknik Evaluasi Pengajaran. PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Puspendik. (2019). Laporan Hasil Ujian Nasional. Kemendikbud.
Putri, G. S. (2020). WHO ResmiSebut Virus Corona Covid-19 sebagai Pandemi Global. https://www.kompas.com/sains/read/2020/03/12/083129823/who-resmi-sebut-virus-corona-covid-19-sebagai-pandemi-global?page=all
Rafique, G. M., Mahmood, K., Warraich, N. F., & Rehman, S. U. (2021). Readiness for Daring Learning during COVID-19 pandemic: A survey of Pakistani LIS students. Journal of Academic Librarianship, 47(3), 102346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2021.102346
Rahayu, N. K. L. A., & Agustika, G. N. S. (2020). Improving Mathematics Learning Outcomes Through Problem Based Instruction. International Journal of Elementary Education, 4(3), 261. https://doi.org/10.23887/ijee.v4i3.25409
Ramdani, A., Jufri, A. W., & Jamaluddin, J. (2020). Pengembangan Media Pembelajaran Berbasis Android pada Masa Pandemi Covid-19 untuk Meningkatkan Literasi Sains Peserta Didik. Jurnal Kependidikan: Jurnal Hasil Penelitian Dan Kajian Kepustakaan Di Bidang Pendidikan, Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran, 6(3), 433. https://doi.org/10.33394/jk.v6i3.2924
Ray, S., & Srivastava, S. (2020). Virtualization of science education: a lesson from the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Proteins and Proteomics, 11(2), 77–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42485-020-00038-7
Reynaldo, C., Christian, R., Hosea, H., & Gunawan, A. A. S. (2021). Using Video Games to Improve Capabilities in Decision Making and Cognitive Skill: A Literature Review. Procedia Computer Science, 179, 211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.12.027
Ridwan. (2010). Tes Kemampuam Membaca. https://ikfaiz.wordpress.com/2010/10/07/tes-kemampuam-membaca/
Rohmah, U. (2011). Tes intelegensi dan pemanfaatannya dalam dunia pendidikan. Cendekia: Journal of Education and Society, 9(1), 125–139. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.21154/cendekia.v9i1.869
Rudyanto, H. E. (2017). Pengaruh Kemampuan Membaca Pemahaman Terhadap Prestasi Belajar Matematika Pada Pokok Bahasan Soal Cerita Kelas IV. Ibriez : Jurnal Kependidikan Dasar Islam Berbasis Sains, 2(2), 175–182. https://doi.org/10.21154/ibriez.v2i2.34
Sari, E. V. (2020). Hubungan Metacognitive Awereness dan Self efficacy Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa kelas IV SDN Gugus Cakra Kota Semarang. Universitas Negeri Semarang.
Schneider, S. L., & Council, M. L. (2020). Distance learning in the era of COVID-19. Archives of Dermatological Research, 1(1), 3–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-020-02088-9
Schwab, K. (2019). The Global Competitiveness Report 2019 (p. 666). In World Economic Forum. http://www3. weforum. org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019. pdf.
Setiawan, F. A., Arisanty, D., Hastuti, K. P., & Rahman, A. M. (2020). The Effect of Metacognitive Ability on Learning Outcomes of Geography Education Students. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 2(2), 82–90. https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v2i2.9257
Solihat, E. (2010). Pengaruh Pendekatan open-ended Terhadap Kemampuan Berpikir Kreatif Siswa Dalam Belajar Matematika. UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Stankov, L. (2000). Complexity, metacognition, and fluid intelligence. Intelligence, 28(2), 121–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-2896(99)00033-1
Subekti, F. D. (2016). Hubungan Kemampuan Membaca Dengan Kemampuan Pemecahan Soal Cerita Matematika Siswa. Basic Education, 5(10), 1–9.
Suharnan, M. S. (2005). Psikologi Kognitif. Srikandi.
Sukardjo, M., & Salam, M. (2020). Effect of concept attainment models and self-directed learning (SDL) on mathematics learning outcomes. International Journal of Instruction, 13(3), 275–292. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2020.13319a
Suri, R., & Monroe, K. B. (2001). The effects of need for cognition and trait anxiety on price acceptability. Psychology & Marketing, 18(1), 21-42
Suryaningtyas, S., & Setyaningrum, W. (2020). Analisis Kemampuan Metakognitif Siswa SMA Kelas XI Program IPA dalam Pemecahan Masalah Matematika. Jurnal Riset Pendidikan Matematika, 7(1), 74–87.
Susilowati, N. I. (2012). Korelasi Antara Intelegensi, Motivasi, dan Minat dengan Hasil Belajar. Universitas Negeri Malang.
Tayibu, N. Q. (2016). Pengaruh Intelegensi, Task Commitment Dan Self Efficacy Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa Sma. Journal of Educational Science and Technology (EST), 2(3), 132. https://doi.org/10.26858/est.v2i3.2104
Tohir, M., Abidin, Z., Dafik, D., & Hobri, H. (2018). Students creative thinking skills in solving two dimensional arithmetic series through research-based learning. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1008(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1008/1/012072
Trakulphadetkrai, N. V., Courtney, L., Clenton, J., Treffers-Daller, J., & Tsakalaki, A. (2020). The contribution of general language ability, reading comprehension and working memory to mathematics achievement among children with English as additional language (EAL): an exploratory study. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism, 23(4), 473–487. https://doi.org/10.1080/13670050.2017.1373742
Utari, R. (2013). Taksonomi Bloom Apa dan Bagaimana Menggunakannya. Pusdiklat KNPK.
Veenman, M. V. J., Wilhelm, P., & Beishuizen, J. J. (2004). The relation between intellectual and metacognitive skills from a developmental perspective. Learning and Instruction, 14(1), 89–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2003.10.004
Vista, A. (2013). The role of reading comprehension in maths achievement growth: Investigating the magnitude and mechanism of the mediating effect on maths achievement in Australian classrooms. International Journal of Educational Research, 62, 21-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2013.06.009
Vittadinic, G., Sturarob, C., & Folloni, G. (2021). Non-Cognitive Skills and Cognitive Skills to measure school efficiency. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 101058, 1–5.
Wahyuddin. (2016). Pengaruh Metakognisi, Motivasi Belajar, Dan Kreativitas Belajar Terhadap Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Siswa Kelas Viii Smp Negeri 2 Sabbangparu Kabupaten Wajo. Jurnal Daya Matematis, 4(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.26858/jds.v4i1.2453
Wahyuddin, Maharida, Jusriadi, E., & Syafaruddin. (2020). Analysis of Motivation and How The Students Learn in Pandemic. Pedagogia : Jurnal Pendidikan, 9(2), 259–273. https://doi.org/10.21070/pedagogia.v9i2.570
Walgito, B. (2010). Bimbingan dan konseling (Studi dan Karir). CV Andi Offset.
Wihasta Jagat Wicaksana, M., Baidowi, B., Kurniawan, E., & Turmuzi, M. (2021). Pengaruh Motivasi dan Kecemasan Belajar Matematika Terhadap Kesadaran Metakognisi dan Kaitannya dengan Hasil Belajar Matematika. Griya Journal of Mathematics Education and Application, 1(1), 81–89. https://doi.org/10.29303/griya.v1i1.11
Wimbarti, S. (2000). Bunga Rampai Psikologi Pendidikan. Fakultas Psikologi UGM.
World Economic Forum. (2020). The Future of Jobs Report 2020, World Economic Forum. In Research Report (Issue October). World Economic Forum.
Yahya, A., & Bakri, W. N. (2020). Pembelajaran kooperatif tipe rotating trio exchange untuk meningkatkan aktivitas dan hasil belajar matematika siswa. Jurnal Analisa, 6(1), 69–79.
Zahra, A. S., & Wijayanti, S. (2020). Efektivitas Pembelajaran Basis Daring di Lain Tulungagung Dengan Adanya Kebijakan Physical Distancing Era Pandemi Covid 19. Geram (Gerakan Aktif Menulis), 8(1), 83–89.
Zamista, A. A., & Kaniawati, I. (2016). Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning Terhadap Keterampilan Proses Sains Dan Kemampuan Kognitif Siswa Pada Mata Pelajaran Fisika. Edusains, 7(2), 191–201. https://doi.org/10.15408/es.v7i2.1815
Copyright (c) 2022 Wahyuddin Wahyuddin, Muhammad Awal Nur, Sri Satriani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
License and Copyright Agreement
By submitting a manuscript to Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (JUPITEK), the author(s) certify and agree to the following terms:
- Originality and Authority: The submitting author is authorized by all co-authors to enter into this agreement. The manuscript describes original work that has not been published previously in a peer-reviewed journal, nor is it under consideration for publication elsewhere.
- Approval: Its publication has been approved by all author(s) and by the responsible authorities of the institutions where the work was carried out.
- Rights: The authors secure the right to reproduce any material that has already been published or copyrighted elsewhere.
- Licensing and Copyright: Authors retain the copyright to their work.
- License Grant: The authors grant Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (JUPITEK) the right of first publication, with the work simultaneously licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).
- Self-Archiving: Authors are permitted and encouraged to deposit the published version of their article in institutional repositories, on their personal websites, and other academic platforms, with proper acknowledgment of its initial publication in Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika (JUPITEK).





.png)


